Welcome to our blog on the ATP cycle! ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that plays a crucial role in the energy metabolism of cells. It is the main source of energy for many biological processes. These include contracting muscles, sending nerve impulses, and making new parts of cells. In this blog, we will explore the ATP cycle. This cycle is the process by which ATP is synthesized. Cells use this cycle to synthesize ATP.
Cellular respiration, a process in the mitochondria of cells, initiates the ATP cycle. Cells make ATP by breaking down glucose and other nutrients to obtain energy. We then use this energy to produce more ATP. Once produced, ATP powers a wide range of biological processes. These processes include muscle contraction and the synthesis of proteins and other cell components.
But the ATP cycle doesn’t stop there. When ATP is used, it is turned back into its precursor, ADP (adenosine diphosphate), which releases energy. This allows cells to recycle ATP and use it over and over again to power their functions.
Cells typically use free energy from the environment for various purposes. Phototrophs, like plants, get this energy from the sun. Chemotrophs, like bacteria, obtain it from other places. They get energy when they break down organic compounds. ATP, a molecule that carries energy in a unique way, transforms some of this free energy.
ATP is a key part of how cells move energy from processes that make energy to processes that use energy. When ATP is used, it breaks down into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and Pi (inorganic phosphate), releasing energy in the process. We use this energy for various functions like synthesising macromolecules, transporting ions and molecules, and performing mechanical work.
This blog will explain the ATP cycle, including how cells produce and use ATP and its role in energy metabolism. We will also discuss the importance of the ATP cycle. It helps in keeping cells and organisms healthy. It ensures they work well as a whole. So join us as we explore the fascinating world of ATP and its role in the energy metabolism of cells!
Table of Contents
Formation and expenditure of ATP
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and a phosphate group combine to form ATP, as shown in the following chemical equation:
ADP + Pi + energy → ATP
Here, Pi represents a phosphate group. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of cells. It breaks down glucose and other nutrients. This process makes the energy needed for this reaction.
The following chemical equation represents the expenditure of ATP to release energy:
ATP → ADP + Pi + energy
This reaction releases energy by converting ATP back into ADP. Cells can use this energy for many different things. They can use it for contracting muscles, sending nerve impulses, and making new parts of cells.
Making and using ATP are crucial components of the ATP cycle. The cycle is the process by which cells generate and utilize ATP. The ATP cycle allows cells to recycle ATP and use it over and over again to power their functions.
What are the similarities between ATP molecule and rechargeable batteries?
ATP and rechargeable batteries have several similarities:
- Both ATP and rechargeable batteries store and release energy. Rechargeable batteries store energy through the movement of electrons. They release electrical energy in a similar manner. ATP stores energy and releases it when it breaks down into ADP and Pi.
- Both ATP and rechargeable batteries can be used and reused. Cells constantly synthesize and use ATP, recycling it back into ATP through the ATP cycle. Similarly, cells can use and recharge rechargeable batteries multiple times before they require replacement.
- Both ATP and rechargeable batteries are essential for powering a variety of functions. Rechargeable batteries power a wide range of devices. These include cell phones, laptops, and electric vehicles. ATP serves as the primary energy source for many cellular processes.
- Both ATP and rechargeable batteries have limited capacity. Cells have a limited capacity to store ATP, and upon its depletion, they must synthesize extra ATP. Similarly, rechargeable batteries have a limited capacity to store and release energy, necessitating recharging when they deplete.
ATP and rechargeable batteries are similar in many ways. Both store and release energy. We can use and reuse them. A wide range of functions require their power. However, humans make rechargeable batteries, while living things produce ATP.
Structure of Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a nucleotide molecule that is crucial for the body’s use of energy.
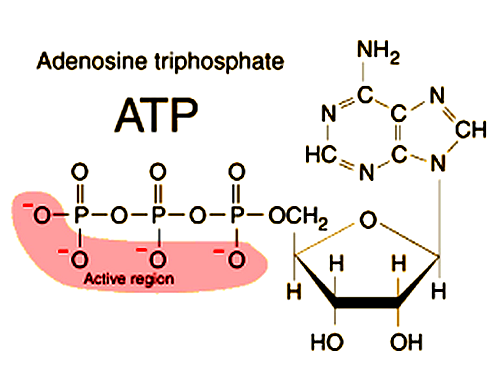
It consists of three major components:
- Adenine: DNA and RNA contain adenine, a nitrogenous base. It consists of a six-membered ring, each containing five carbon and nitrogen atoms.
- Ribose: Ribose is a five-carbon sugar that is found in RNA. It is composed of a five-membered ring with four atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen.
- Phosphate groups: ATP has three phosphate groups attached to the ribose sugar. Each phosphate group consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms.
The structure of ATP is important because it allows the molecule to store and release energy. The bonds between the phosphate groups store the energy. Removing one of the phosphate groups releases the energy. This process forms ADP (adenosine diphosphate).
This process, called hydrolysis, releases energy that can be used by cells for various purposes.
Overall, the structure of ATP is extremely complex, and it plays a crucial role in the use of energy. It is the main source of energy for many cellular processes, which shows how important it is to life.
Important point on ATP
- ATP is a nucleotide molecule that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism.
- It is composed of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups.
- The energy stored in ATP is released when one of the phosphate groups is removed, forming ADP.
- ATP is produced through a process called cellular respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
- ATP is the primary source of energy for many cellular processes. These include muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and the synthesis of cellular components.
- The ATP cycle allows for the recycling of used ATP back into ATP.
- The structure of ATP is important because it allows the molecule to store and release energy.
- ATP is vital to life. Cells require it to function. Organisms also depend on it to work.
ATP cycle: ATP-ADP Cycle
The ATP cycle is also called the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) cycle or the phosphagen system. It is how cells make ATP. ATP is the main source of energy for most cellular activities. ATP is a high-energy molecule. It stores energy in the form of chemical bonds. These bonds can be broken down and used to fuel various cellular activities.
The ATP cycle begins when ATP is broken down into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate molecule (Pi). This process gives off energy. Cells can use this energy to do different things. These include contracting muscles, making proteins and lipids, and moving molecules across cell membranes.
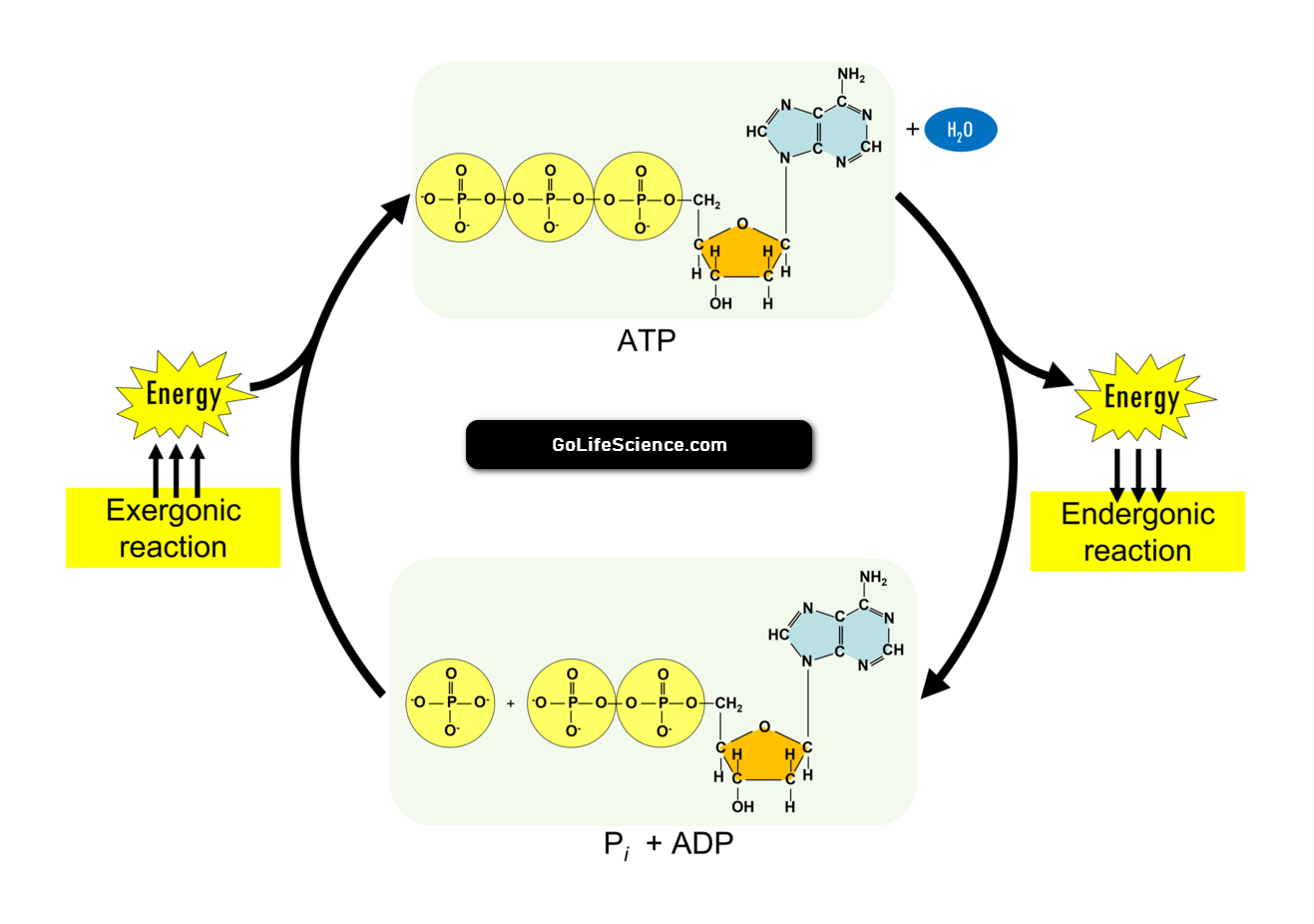
The body breaks down glucose and other nutrients to get the energy it needs for this process. During cellular respiration, glucose and other nutrients are broken down in the mitochondria to produce ATP. This process happens in three steps: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Kreb’s cycle), the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation.
The first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis, which happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. The breakdown of glucose triggers this process. This process produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, and two molecules of NADH.
The Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle, happens in the mitochondria. It breaks down pyruvate into CO2, ATP, NADH, and FADH2 as byproducts.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the last step of cellular respiration. It happens in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. During this process, electrons are moved from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. Chemiosmosis produces ATP and produces water as a byproduct.
ATP can be made in other ways besides cellular respiration. For example, fat breaks down in muscle cells. ATP breaks down in the myosin heads when muscles contract.
The ATP cycle is essential. It plays a key role in making ATP. ATP is the main energy source for most cellular processes. Without ATP, cells would be incapable of carrying out their functions, and the body would be incapable of sustaining life.
- Top 10 Fastest Flying Birds in the World
- Nucleic Acids : Basics and Types
- Proteins : Basic and Structural organization
- What is the clinical significance of purine metabolism?
Role of ATP in Biological reactions
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is an important molecule in biology that plays a central role in energy metabolism. It is the main energy source for cellular processes. These include contracting muscles, sending nerve impulses, and creating new cell components.
- ATP serves as an energy currency for cells. It stores energy in chemical bonds. These bonds can be broken down and used to fuel various cellular processes.
- We use ATP to drive endergonic reactions, which are chemical reactions that require an energy input to proceed. These reactions include the synthesis of proteins and lipids, the transport of molecules across cell membranes, and muscle contraction.
- ATP is also used to regenerate other high-energy molecules. Examples include NADH and FADH2. These molecules are used in the production of ATP during cellular respiration.
- ATP plays a role in the regulation of enzyme activity. Some enzymes require the presence of ATP to function properly. Others are either activated or inhibited by ATP.
- ATP is involved in the regulation of gene expression. It can bind to specific regulatory proteins. This binding affects their activity. It leads to changes in gene expression. This, in turn, results in the production of specific proteins.
- ATP plays a role in signaling pathways within cells. Cells can release it. Then it binds to receptors on the surface of other cells. This binding triggers a signaling cascade that leads to specific cellular responses.
- ATP is involved in the maintenance of ion gradients across cell membranes. It pumps ions, like potassium and calcium, across cell membranes to maintain the proper balance of ions within cells.
- ATP is also involved in the regulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis (programmed cell death). It can affect the activity of enzymes and regulatory proteins that control these processes.