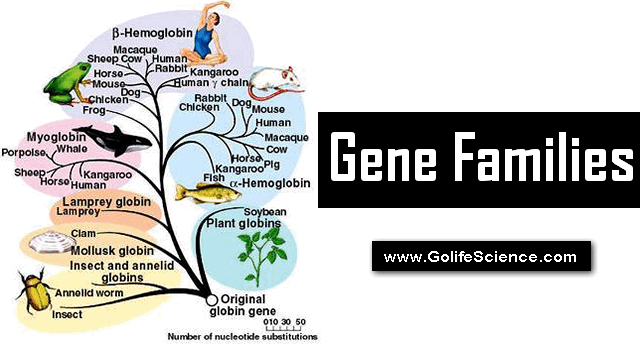
Gene families are teams of DNA segments that have developed by frequent descent by duplication and divergence. They’re a number of DNA segments that have developed from one widespread ancestral DNA phase that has been copied and altered over hundreds of thousands of years.
- What is the Fidelity of DNA Replication in Normal?
- Deoxyribonucleic acid its Types: A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA
- DNA Replication: Simple Steps of DNA replication in E.Coli

Table of Contents
What are Gene Families?
The members of a gene family might embody expressed genes in addition to non-expressed sequences. Such non-expressed sequences embody promoters, operators, transposable genetic components, and pseudogenes, which are genes that can be not functionally expressed.
- Pseudogenes resemble different relations of their linear sequence of nucleotides. Nevertheless, they often both lack the indicators that may enable them to be expressed or have vital deletions or rearrangements that forestall profitable transcription or translation.
- One well-studied gene family is that of the globins. The globin family incorporates many pseudogenes in addition to many useful genes, together with the genes coding for hemoglobins (α, β, γ, δ).
- Gene families in vegetation range enormously in dimension and quantity, ranging, within the human genome, from only a few copies of very carefully associated sequences to greater than a half-million copies of Alu sequences, that are transposable genetic components with no identified operate. For genes that encode proteins, duplicate copies of genes have been discovered for over 2,000 proteins in a wide range of genomes.
- Members of gene families could also be positioned in contiguous clusters on one chromosome, or they could be scattered all through a genome.
- Homeotic genes, which lie in contiguous clusters on a couple of chromosomes, present the very best instance of evolutionarily preserved gene order inside a gene family.
- These genes play a task within the spatial improvement of the anterior-posterior axis of vertebrates and invertebrates. 4 binary axes are laid down early within the basal physique plan of most metazoans, together with us: anterior-posterior, dorsal-ventral, left-right, and inside-outside.
- They have an effect on areas on the physique axis in roughly the identical order as they’re organized alongside a chromosome, although totally different gene families and clusters seem on totally different chromosomes. Amazingly, these genes work about the identical in a fruit fly as they do in a human in establishing linear preparations.
- In some gene families, associated genes have stayed collectively over lengthy intervals of evolution, whereas in different gene families; members have developed into broadly distributed inside genomes.
- In ribosomal RNA genes, tandem arrays, through which a number of copies of the identical gene happen one after one other, have been noticed. Then again, within the globin gene family, each the order and distribution of the genes, which aren’t identical, range broadly, even inside one taxonomic group such because of the mammals.
- Members of a gene family often have comparable constructions, however, they could have diverged evolutionarily to such an extent that they’re expressed in several methods.
- They could be expressed on totally different occasions within the improvement of multi-cellular organs or in several cells and tissues, they usually could have acquired totally different features.
- They could even have been transferred between organisms that aren’t carefully associated with evolution.
One controversy about gene families includes whether or not they have arisen primarily by polyploidy or through tandem gene duplications. Polyploidy signifies that full genomes in an organism are duplicated both by mitosis or meiosis without cytokinesis or by matings between organisms with unequal numbers of chromosomes.
That is adopted by full copying of each dad and mom’s full genomes so every haploid set of chromosomes is now diploid. In a tandem duplication, a number of copies of a gene lie on the identical chromosome adjoining to 1 one other. Polyploidy has been invoked to elucidate the evolution of advanced new features in taxa. Researchers give 5 causes.
Polyploids
- It has “larger ranges of heterozygosity than do their diploid dad and mom”;
- It reveals much less inbreeding despair than do their diploid dad and mom.
- They’re polyphyletic incorporates genetic range from a number of “progenitor populations” and, thus, they’ve larger genetic range “than anticipated by fashions of polyploid formation involving a single origin”;
- It has genome rearrangements which can be widespread; and
- They’re like duplicated genes, free of intense choice strain, which permits frequent evolution of latest features
Austin Hughes has been the key critic of the usually invoked polyploid speculation for the origin of main animal teams due to the key substitution load that may be concerned and molecular phylogenetic proof in opposition to it.
Nevertheless, the outcomes of most molecular evolutionary research are extra per the gradualist view that new features are generated primarily by tandem gene duplication and divergence of each sequence and performance, unfold over a very long time.






